Learning Objectives
- Differentiate between ingestion, digestion, absorption, and elimination
- Compare and contrast complete and incomplete digestive tracts
- Identify the general functions of digestive tract components
- Describe the diversity of adaptations in digestive tract components for acquisition of nutrients among different animal groups, especially mouth structures, presence of specific digestive system structures, and the role of the gut microbiome in digestion
- Describe the steps of mechanical and chemical digestion, and identify the organs and enzymes required for each step, using humans as a model organism
- Describe the process and location of nutrient absorption, and explain the significance of a large surface area in this process, using humans as a model organism
The Four Steps of Digestion
Animals are chemoheterotrophs, meaning they must obtain both their energy and their carbon from pre-existing organic molecules; animals accomplish these goals by eating which we often think of as equivalent to digestion. In fact, what we think of as “digestion” can be broken down into four discrete steps:
- Ingestion: taking in of food
- Digestion: chemically and mechanically breaking down the food
- Absorption: taking the nutrients from the food into the body
- Elimination: release of waste into the environment
Ingestive feeding is distinct from absorptive feeding, or absorbing nutrients from the environment, which is the feeding process utilized by fungi.
Complete vs Incomplete Digestive Systems
The information below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 34.1
Digestion is the process of breading down tissues of another organism in order to make them available for absorption, and animals can accomplish these processes through two general types of digestive systems:
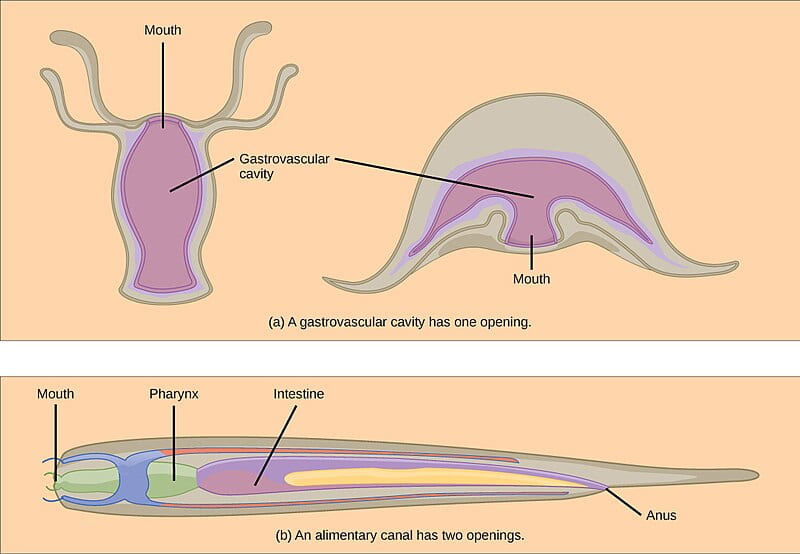
- Incomplete digestive systems (also called a gastrovascular cavity) feature a digestive cavity with a single opening that functions as both mouth and anus.
- Ingested material enters the mouth/anus and passes into a cavity lined with cells that secrete digestive enzymes that break down the food. The food particles are then absorbed by the cells lining the gastrovascular cavity. Once digestion is completed, the remaining material is eliminated as waste through the mouth/anus.
- This type of digestive system is typical of animals with radial symmetry, including Ctenophora (comb jellies) and Cnidaria (coral, jellyfish, and sea anemones).
- Complete digestive systems (also called an alimentary canal) feature a separate opening for the mouth and anus, allowing for both unidirectional movement of food and regional specialization along the digestive tract.
- Ingested material enters the mouth and proceeds to the site of digestion (stomach or gizzard), then the site of nutrient absorption (intestine), and then remaining waste is eliminated through the anus.
- Nearly all bilaterally symmetric animals have a complete digestive tract, with the exception of Platyhelminthes (flatworms) which have an incomplete digestive system.
Overview of Digestive System Components, Functions, and Adaptations
All digestive systems accomplish the same essential functions: intake of food, digestion of food (chemical and/or mechanical) into nutrients, absorption of nutrients (into either a circulatory system or directly into tissues), and elimination of wastes. In this section we will provide an overview of this process in a “generalized” complete digestive system while also pointing out various adaptations to different types of feeding in different animal lineages.
- The mouth is the site of ingestion (taking in food). In some animals, mechanical and/or chemical digestion may also begin in the mouth, but this is not universally true: mechanical digestion can begin in the mouth only if the animal has teeth and a jaw structure adapted for chewing; chemical digestion can begin in the mouth for a subset of nutrients only if the animal produces the appropriate digestive enzymes in the saliva.
- The esophagus transports swallowed food from the mouth to the next site in the digestive tract, which is typically the stomach (though this varies among animal lineages). Depending on the animal, the food could travel next to a crop, a stomach, a gizzard, or a rumen.
- The crop is a location used for storage of food prior to digestion, present in some animals including some bird species and many invertebrates.
- The stomach is typically the location for both mechanical and chemical digestion in most animals. The stomach typically has powerful muscles that mechanically break down the food as the stomach muscles contract, and the stomach also produces digestive enzymes that break down the food into its constituent nutrients.
- The gizzard is an additional location for mechanical breakdown of food which is often present in animals that lack teeth or that have a jaw structure that does not allow for chewing. Gizzards are present in some vertebrates (birds and reptiles) and many invertebrates.
- The rumen is houses symbiotic bacteria and protists capable of digesting grass and other cellulosic material. Rumens are present in a group of hoofed herbivores called ruminants, which include cows, sheep, goats, and other grazing animals.
- After traveling through one or more of the organs listed above, the food travels to the small intestine, which is the last site of chemical digestion and the location where the nutrients are absorbed into the animal’s body. Chemical digestion in the small intestine is mediated by accessory organs including the liver and the pancreas. The small has a massive surface area to support nutrient absorption.
- The cecum is located at the junction between the small and large intestines. In herbivores, the cecum houses symbiotic bacteria capable of digesting cellulose.
- The large intestine is the final location for what was once food: the food has now been digested and the nutrient absorbed, and so the large intestine is not actually involved in digestion. However, it serves several critical roles related to digestion:
- The digestive process requires a significant amount of water: approximately 7 liters of water is secreted into the digestive tract on a daily basis, and the large intestine reabsorbs approximately 90% of this water.
- The colon also reabsorbs salts used in digestion.
- The colon houses an enormous quantity and enormous diversity of the microbes; these microbes contribute to host health both by synthesizing a wide variety of vitamins (including biotin, folic acid, vitamin K, and several B vitamins) and by excluding other competing, and potentially pathogenic, bacteria.
Animal Adaptations for Nutrient Acquisition and Digestion
The information below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 34.0, OpenStax Biology 34.1 OpenStax Biology 34.2
There are many adaptations across animal species to facilitate ingestion and digestion of different food sources, beyond the list of general digestive tract components above.
Example adaptations for ingestion of different foods:
- Invertebrate mouth parts: Invertebrates lack teeth, but demonstrate a wide array of mouth structures that are adapted to different food types; for example, among insects:
- bees have structures that facilitate lapping up of nectar
- grasshoppers have structures to support chewing of vegetation
- butterflies have straw-like structures that allow for siphoning of nectar
- Vertebrate jaw structure: Vertebrate jaw structure varies widely across species; for example, snakes have an extra bone on either side of the jaw, as well as flexible tendons joining the center of the lower jaw, which allow snakes to open their jaws wide enough to swallow prey that appears to be larger than their heads
- Teeth: Among vertebrates with teeth, different types of teeth are adapted to different types of foods:
- Incisors work well for biting
- Canines work well for tearing chunks of food from a larger mass; canines tend to be larger in carnivores
- Molars work well for chewing; molars tend to be flatter and more numerous in herbivores and omnivores
- The crop is a location used for storage of food prior to digestion, present in some animals including some bird species and many invertebrates. The crop is an adaptation that allows animals to eat in excess when a food source is abundant, then store the food for digestion later.
Example adaptations for digestion of different foods:
- Symbiotic microorganisms: the digestive tract of all animals contain symbiotic microorganisms which perform their own digestion of food within the animal. In most cases, the relationship is mutually beneficial: the microorganisms have a steady supply of nutrition and live within a controlled environment protected from predators, and the animal has access to the nutrient byproducts produced by the microorganisms as a result of their digestive activities. In fact, many vitamins and other nutrients, such as vitamin K, are inaccessible in food materials until released by the digestive activity of symbiotic bacteria in an animal’s gut.
- Cecum and rumen: digestion of plant material requires additional steps and is far less efficient compared to digestion of animal material; in addition, some digestive steps of plant materials can only be performed by microorganisms. Herbivores have a variety of adaptations to house and support specific symbiotic bacteria within their digestive tract; in turn, these bacteria ferment plant fibers and other plant material which releases nutrients which would otherwise be unavailable to the animal. This process provides nutrients to the bacteria and also makes more nutrients available to the animal host. These digestive structures include:
- a large cecum (present in non-ruminant herbivores, such as rabbits and other herbivorous rodents), which is a pouch-like structure at the junction of the small and large intestines that houses symbiotic bacteria capable of digesting cellulose (the appendix is the vestigial cecum in humans)
- a rumen and associated organs (present in ruminant herbivores, such as cows), which is essentially a fermentation vat within the digestive tract to house symbiotic bacteria and protists capable of digesting cellulose The rumen maintains an anaerobic environment and houses symbiotic bacteria and protists capable of digesting cellulose. Rumens and several accessory digestive organs (including the reticulum, the omasum, and the abomasum) are present in a group of hoofed herbivores called ruminants, which include cows, sheep, goats, and other grazing animals.
- Gizzard: in both invertebrates and vertebrates that lack teeth entirely (such as birds) or teeth/jaw structure to support chewing (such as many reptiles), the gizzard is often the side of mechanical breakdown of food. The gizzard is a stomach-like chamber that combines powerful muscle contractions as well as small pebbles, sand, or grit eaten by the animal to mechanically break down food items to facilitate their digestion.
Digestion: Enzymes and Organs
The information below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 34.3 and Khan Academy: The digestive and excretory systems review. All Khan Academy content is available for free at www.khanacademy.org
Digestion involves both mechanical (physical) disruption of food items as well as chemical (usually enzymatic) breakdown of food into molecular subunits. These processes are carefully coordinated across multiple physical locations in animals with complete digestive tracts; here we will detail this process using humans as a model organism:
The process of chemical and mechanical digestion in humans begins in the mouth, followed by the stomach, and finally the small intestine:

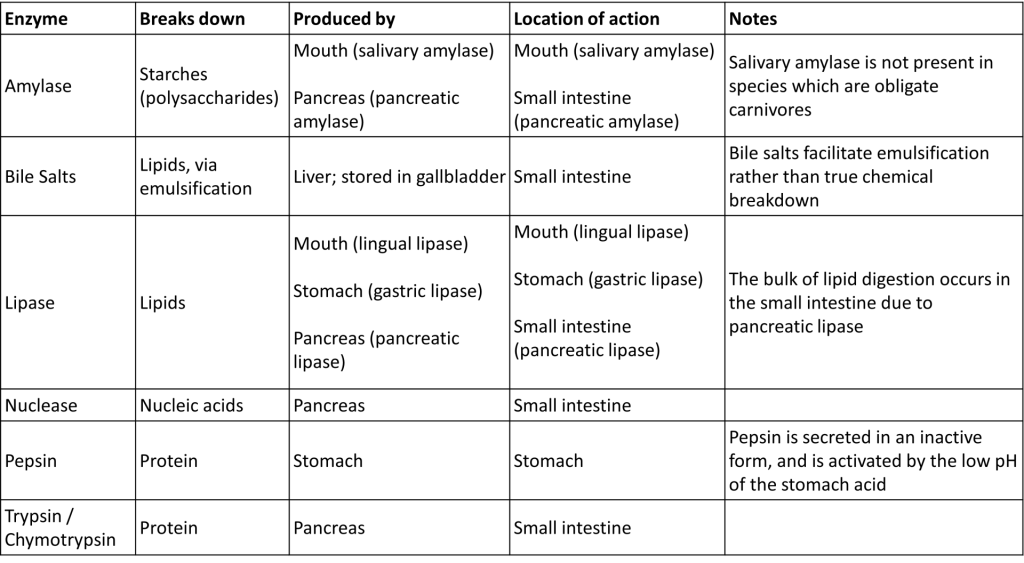
The process of digestion requires multiple enzymes, each of which digest specific types of nutrients, and which are introduced at varying steps in the digestion process. The table below lists a subset of the enzymes involved in digestion in humans (there are many others not included here):
The digestive process in humans follows a stepwise process, outlined below:
- Digestion begins when food enters the mouth, also called the oral cavity. Both mechanical and chemical digestion occur in the mouth:
- The teeth grind and break up food, supported by the activity of the tongue
- Salivary amylase begins to break down carbohydrates
- Lingual lipase begins to break down fats
- After it is swallowed, the chewed food (now called a bolus) moves down the esophagus. The esophagus acts as a connection between the mouth and the stomach, but no digestion occurs here.
- The bolus then reaches the stomach, where more mechanical and chemical digestion take place. Digestion in the stomach continues for several hours, during which:
- The muscles in the stomach walls churn the bolus
- As it churns, the bolus mixes with gastric acids (stomach acid; pH between 1.5 and 2.5) combined with enzymes including gastric lipase (breaks down fats) and pepsin (breaks down proteins). Importantly, the stomach is lined with a layer of protective mucus, that effectively insulates the stomach cells from direct contact with the gastric acids and digestive enzymes.
- These processes together convert the bolus into a liquid called chyme.
- The chyme is slowly transported into the small intestine, where the majority of chemical digestion takes place. No mechanical breakdown occurs in the small intestine. The small intestine does not produce any digestive enzymes, and instead relies on several critical accessory organs:
- The pancreas releases multiple digestive enzymes including pancreatic amylase (breaks down starches), nuclease (breaks down nucleic acids), trypsin (breaks down proteins, among many other proteinases secreted by pancreas) and pancreatic lipase (breaks down lipids)
- Bile salts (produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder) are released to support digestion of fats by promoting emulsification, which is the breakdown of larger lipid “globules” into smaller globules. The resulting small globules are more widely distributed in the chyme rather than forming large aggregates, which increases the available surface area of fat molecules to facilitate both digestion and absorption.
Nutrient Absorption
Digestion is a chemically hazardous process, because the food an animal eats could be chemically indistinguishable from the animal’s own body tissues; thus digestion is a carefully regulated process that effectively takes place outside of the body. Once digestion is completed, the nutrients must then be absorbed from outside of the body into the body’s tissues. This process takes place in the small intestine.
The small intestine has several important features that facilitate nutrient absorption:
- The lining of the small intestine is highly folded; and each fold has multiple structures called villi (singular: villus), and each villus has multiple micro-projections called microvilli. As a result, the total surface area of the human small intestine is approximately 260-300 m2 (approximately the size of a typical tennis court).
- Close to the surface within each villus is a network of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels, which minimize the distance required for absorption of nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Blood vessels absorb sugars and amino acids via facilitated diffusion or cotransport
- The lymphatic system absorbs digested lipids via a process called exocytosis

Absorption of sugars and amino acids is fairly straightforward: these nutrients are absorbed into the villi and then into the blood vessels within the villi via facilitated diffusion or cotransport, depending on the nutrient.
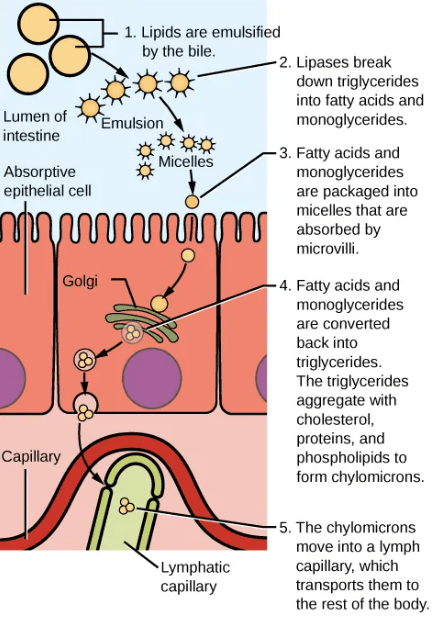
Absorption of lipids is more complex, as they are not soluble in the aqueous environment. The digested fats form into small spheres called micelles, which diffuse into which are then coated in proteins to form larger spheres called chylomicrons. The chylomicrons contain a mix of different types of digested lipids. Chylomicrons are then transported from the villi into the lymphatic system via a process called exocytosis.
The video below provides a characteristically Hank Green overview of animal digestion, highlighting many of the processes and structures described above:

